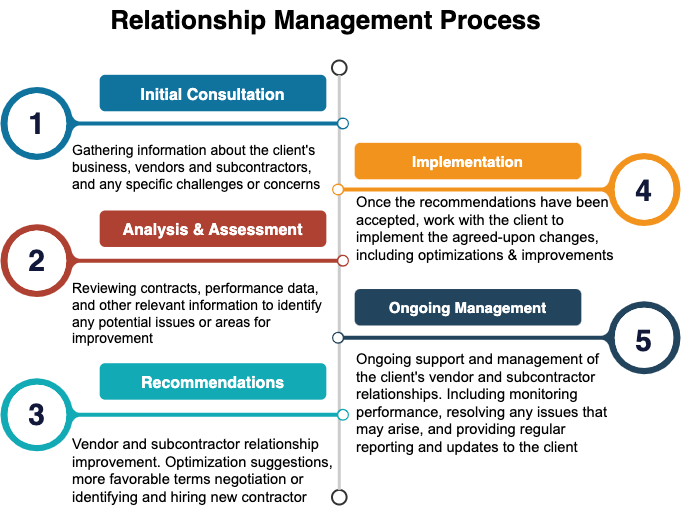
Lean
Lean is a management philosophy and set of principles that focus on maximizing value, eliminating waste, and continuously improving processes and systems for optimizing the flow of value in a business or organization. It originated in the automotive industry, but has since been applied to many other industries.
The core principles of Lean include:
Identifying and maximizing value from the perspective of the customer
Eliminating waste, including activities that do not add value
Continuously improving processes and systems
Lean also emphasizes collaboration and cross-functional teamwork, as well as using data and metrics to drive decision-making. The goal of Lean is to create a culture of continuous improvement, where employees at all levels are empowered to identify and eliminate waste and inefficiencies.
When To Choose Lean?
It is a good approach to use in situations where you need to deliver high-value work quickly and efficiently, and where you need to maximize value and minimize waste.
Lean is particularly well-suited to projects with complex or uncertain requirements, where the team needs to be flexible and adaptable in order to navigate the complexity and uncertainty. It is also well-suited to projects where collaboration and communication are important, and where the team needs to work closely with stakeholders and customers.
Lean is not well-suited to projects with well-defined requirements, where the team can deliver high-value work quickly and efficiently using a more structured and disciplined approach, such as Scrum or SAFe®. In these cases, a more flexible and adaptable approach, such as Scrum or Scrumban, may be more appropriate.
Lean pros and cons
Pros:
Lean emphasizes the importance of maximizing value and minimizing waste, which can help organizations to be more efficient and effective.
Lean promotes collaboration and communication, as it encourages teams to work together and share information and knowledge.
Lean encourages the use of data and metrics to drive decision-making, which can provide valuable insights into the performance and efficiency of the organization.
Lean supports the continuous improvement of processes, which can help organizations to continually evolve and adapt to changing circumstances.
Cons:
The adoption of Lean can require a significant cultural shift within an organization, which can be challenging and time-consuming to implement.
Lean can be difficult to manage, as it involves coordinating the efforts of multiple teams and stakeholders.
Lean can be complex, especially for organizations with large and legacy systems, which can make it difficult to implement and maintain.
Lean can require a significant investment in tools and technologies, which can be expensive and may not be feasible for all organizations.
People Also Viewed